Rotary Dryer

Rotary dryer or rotary drum dryer is widely used to dry humidity granularity materials in the industries of mineral dressing, building material, metallurgy and chemical, coal mining, etc. Wide supply scope and simple operation are its main features, materials should be dried to 3-10% water content to meet the demands for briquetting.
Application
Coal, coke
Clays, phosphates
Starch Pulp
Minerals, fertilizers
Beet pulp
Floatation concentrates
Animal feeds
Germ, stillage
Sludges
Etc.
Rotary drying line
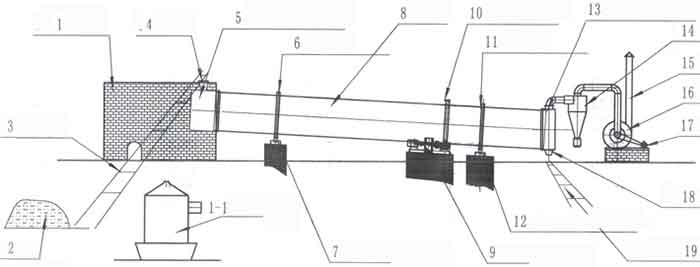
1-1. Gas Stove
2. Materials
3. Feeding Conveyor
4. Inlet
6. Roller Ring
7. Carrier Roller
8. Drum
9. Transmission
11. Roller Ring
12. Carrier Roller
13. Discharge Cover
14. Dust Collector
16. Induced Draft Fan
17. Motor
18. Outlet
19. Discharging Conveyor
How it works
The material is fed in the rotary drum dryer by the conveyor, and when it’s coming through the cylinder, the hot air will flow from it and makes it dried,. The dried material will be collected at the output.
In this drying process, the material will move as the cylinder rotation. With the gravity, the material will fall from high-end to low-end. There are also copy boards in the dryer to raise the material, so that the material and hot air’s contact surface area increases, which helps to increase the drying rate and let the material forward.
After drying, the fine particles are collected by the dust collector and the exhaust gas is discharged by the dust collector.
Details show
 inside
inside drum
drum riding wheel
riding wheel cover plate
cover plateHeat Source
gas, diesel, coal, wood, steam, etc.
Drying way
- Parallel flow: The wettest material comes in contact with the hottest gas as they enter the dryer. This results in a rapid evaporation and rapid cooling of the hot process gas. This typically allows the dryer shell to operate slightly cooler than the counter-flow configuration, which extends the life cycle and decreases maintenance of the dryer.
Features for parallel flow:
1. At the input area, the hot air is much higher than the raw material which leads a rapid heat exchange between the hot air and the raw material, moisture becomes easy to evaporate. This heat way is suitable for high moisture materials.
2. For the viscous materials, when it feeds into the dryer, as the rapid water evaporates, the moisture down and helps to reduce the bonding rate, the easier-move material increase the drying efficiency.
3. The low negative pressure in the feeding place leads to low air leakage from the input, thus keeps the hot air in the dryer steadier with the temperature and the velocity.
- Counterflow: Wet material is introduced into the drum on the opposite end that the hot gas enters the dryer and dry material discharges on the opposite end of the dryer as the exhaust vapour.
Features for counter flow:
1. Suitable for material with low moisture and low heat sensitive.
2. The drying rate is evenly distributed. So counter flow is more suitable for material which is strict with the final moisture.
3. Low dust. As the heating air move from the dry end to the wet end, as the function of the wet air, there will be less dust in the exhaust.
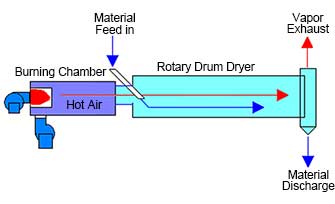 cocurrent dryer (Parallel flow)
cocurrent dryer (Parallel flow)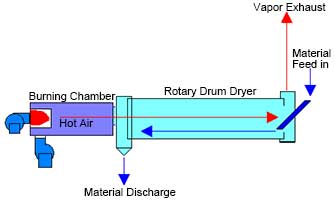 counter current dryer (Counter flow)
counter current dryer (Counter flow)Note: The heating way depends on the requirement of the final product.
Features for rotary drum dryer
Compare to other drying machines, the rotary dryer has advantages as follow:
1. With high capacity, continuous production;
2. Simple structure, easy on operating;
3. Low failure rate, low cost of maintenance.
4. The wide range of adaptation, it can be used to dry varies of material even with high adhesion;
5. Flexible operation. The quality of final product won’t be much changed when the capacity changes.
6. Easy to clean.
Parameter
| Model | Gradient (%) | Diameter (mm) | Length (mm) | Speed (rpm) | Power (kw) | Capacity (t/h) | Weight (t) |
| RD0606 | 3-5 | 600 | 6000 | 3-8 | 3 | 0.5-1.5 | 2.9 |
| RD0608 | 3-5 | 600 | 8000 | 3-8 | 4 | 0.6-1.2 | 3.1 |
| RD0808 | 3-5 | 800 | 8000 | 3-8 | 4 | 0.8-2.0 | 3.5 |
| RD0810 | 3-5 | 1000 | 8000 | 3-8 | 4 | 0.8-2.5 | 5.6 |
| RD1010 | 3-5 | 1000 | 10000 | 3-8 | 5.5 | 1.0-3.5 | 6.7 |
| RD1012 | 3-5 | 1000 | 12000 | 3-8 | 5.5 | 1.5-3.5 | 7.2 |
| RD1208 | 3-5 | 1200 | 8000 | 3-8 | 7.5 | 2-4 | 8.8 |
| RD1210 | 3-5 | 1200 | 10000 | 3-8 | 7.5 | 1.8-5 | 9.8 |
| RD1212 | 3-5 | 1200 | 12000 | 3-8 | 11 | 2-6 | 10.5 |
| RD1512 | 3-5 | 1500 | 12000 | 2-6 | 15 | 3.5-9 | 13.5 |
| RD1514 | 3-5 | 1500 | 14000 | 2-6 | 15 | 4-11 | 15.4 |
| RD1812 | 3-5 | 1800 | 12000 | 2-6 | 18.5 | 5-12 | 18.9 |
| RD1814 | 3-5 | 1800 | 14000 | 2-6 | 18.5 | 5-15 | 23.2 |
| RD1820 | 3-5 | 1800 | 20000 | 2-6 | 22 | 8-20 | 26.1 |
| RD2018 | 3-5 | 2000 | 18000 | 2-6 | 30 | 8-23 | 36.5 |
| RD2020 | 3-5 | 2000 | 20000 | 2-6 | 37 | 10-24 | 38.8 |
| RD2218 | 3-5 | 2200 | 18000 | 1.5-6 | 37 | 10-25 | 42.3 |
| RD2220 | 3-5 | 2200 | 20000 | 1.5-6 | 37 | 12-28 | 45.2 |
| RD2420 | 3-5 | 2400 | 20000 | 1.5-5 | 45 | 18-30 | 50.7 |
| RD2820 | 3-5 | 2800 | 20000 | 1.5-5 | 55 | 20-35 | 60.4 |
| RD2824 | 3-5 | 2800 | 24000 | 1.5-5 | 75 | 25-35 | 70.4 |
| RD3020 | 3-5 | 3000 | 20000 | 1.5-5 | 75 | 25-40 | 78.2 |
| RD3025 | 3-5 | 3000 | 25000 | 1.5-5 | 75 | 30-45 | 104.9 |





